Blog
The ECDB Blog turns data from the Tool into eCommerce insights that illustrate which use you can make of our comprehensive data. It elaborates on relevant eCommerce news to help your brand gain a broader perspective on current retail trends and their effects. Our articles are carefully crafted to present to you the latest market trends, including retail, payment, shipping, transactions, cross-border and more.
Item 1 of 5
All Articles

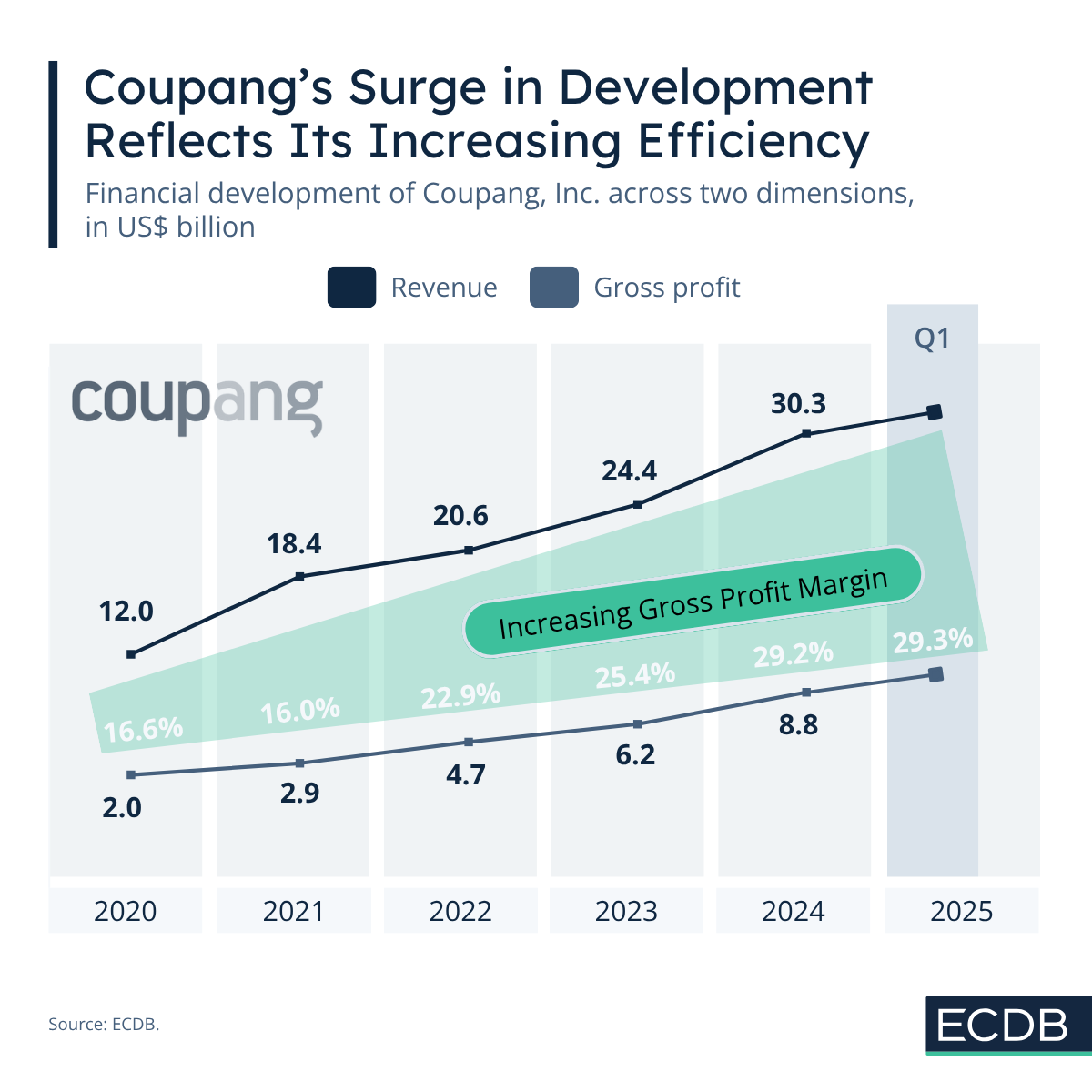
Coupang’s Investments Pay Off: Its Q1 2025 Company Results Indicate Growing Efficiency
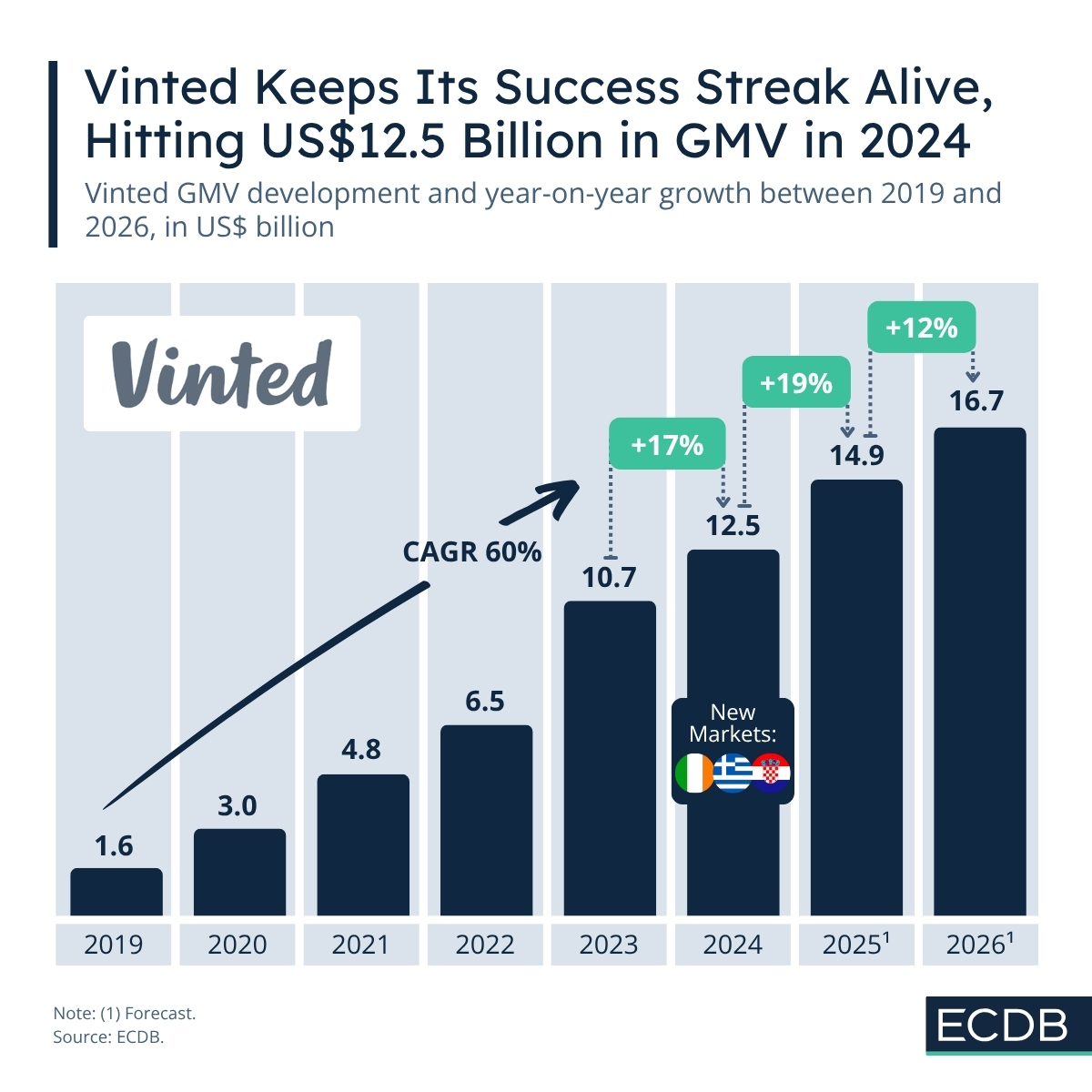
Vinted’s Winning Formula: Fashion, Logistics, Payments, and the Future of reCommerce
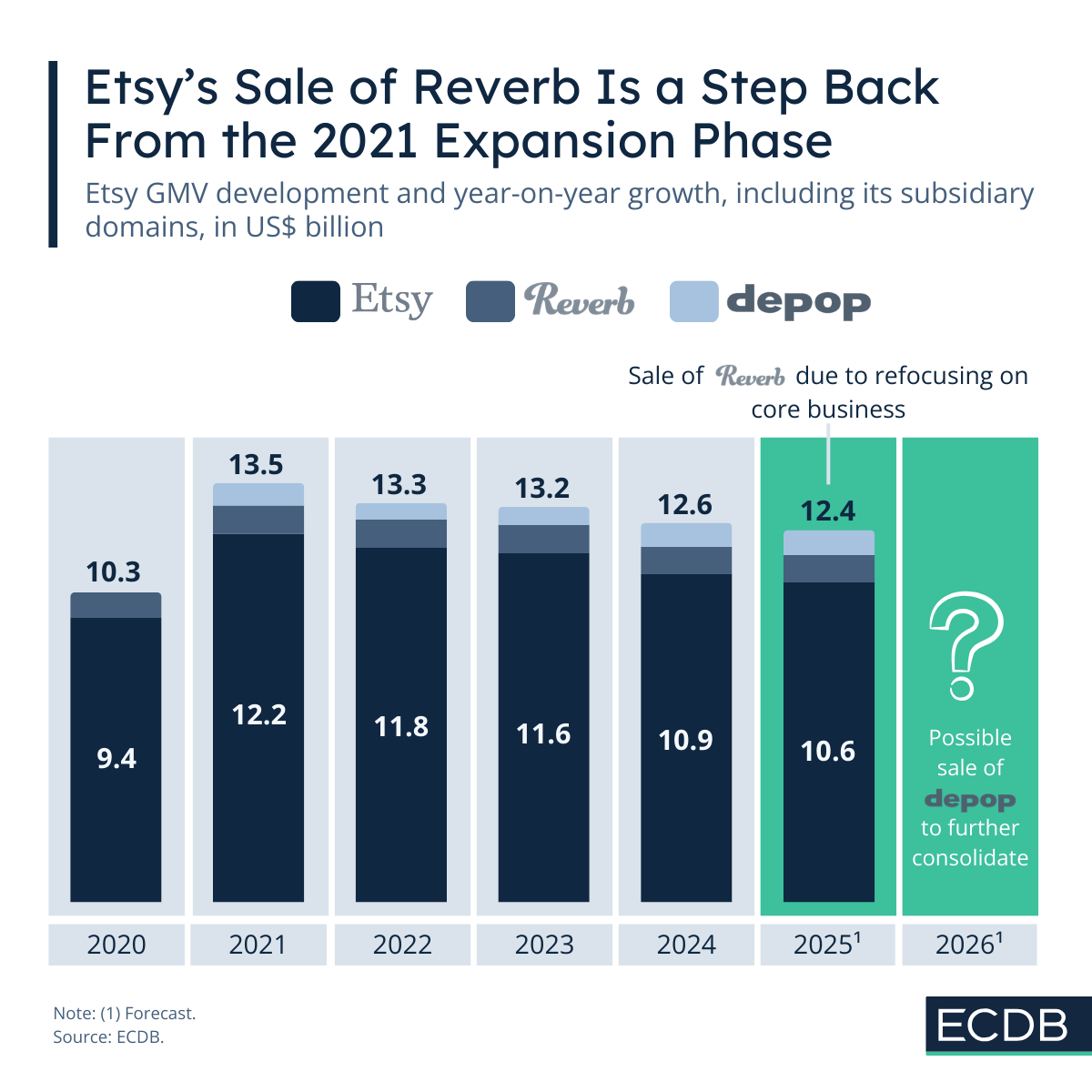
What Does Etsy’s Sale of Reverb Say About Its Position in the Global Market?
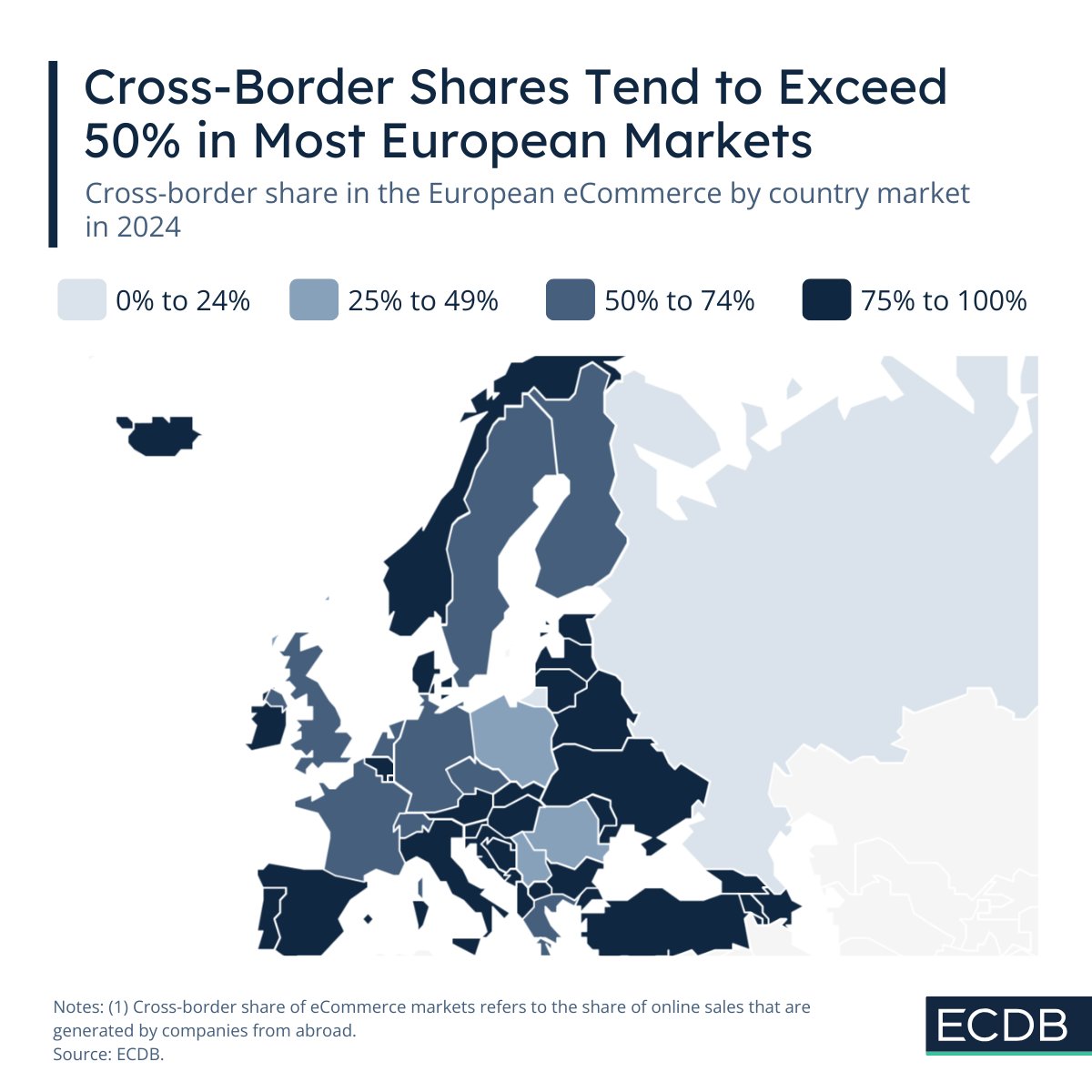
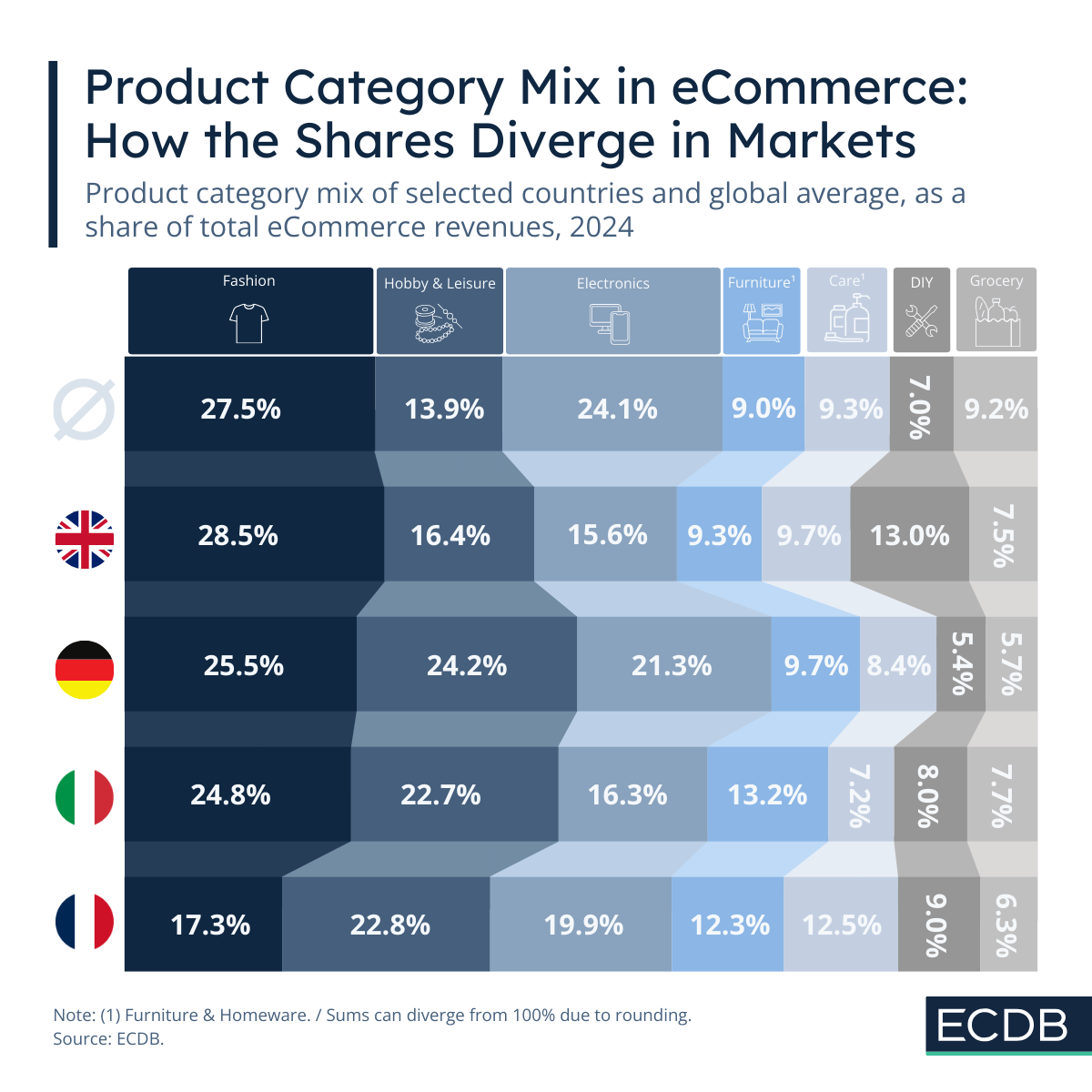
Where Countries in Europe Rely Most on International Companies for eCommerce
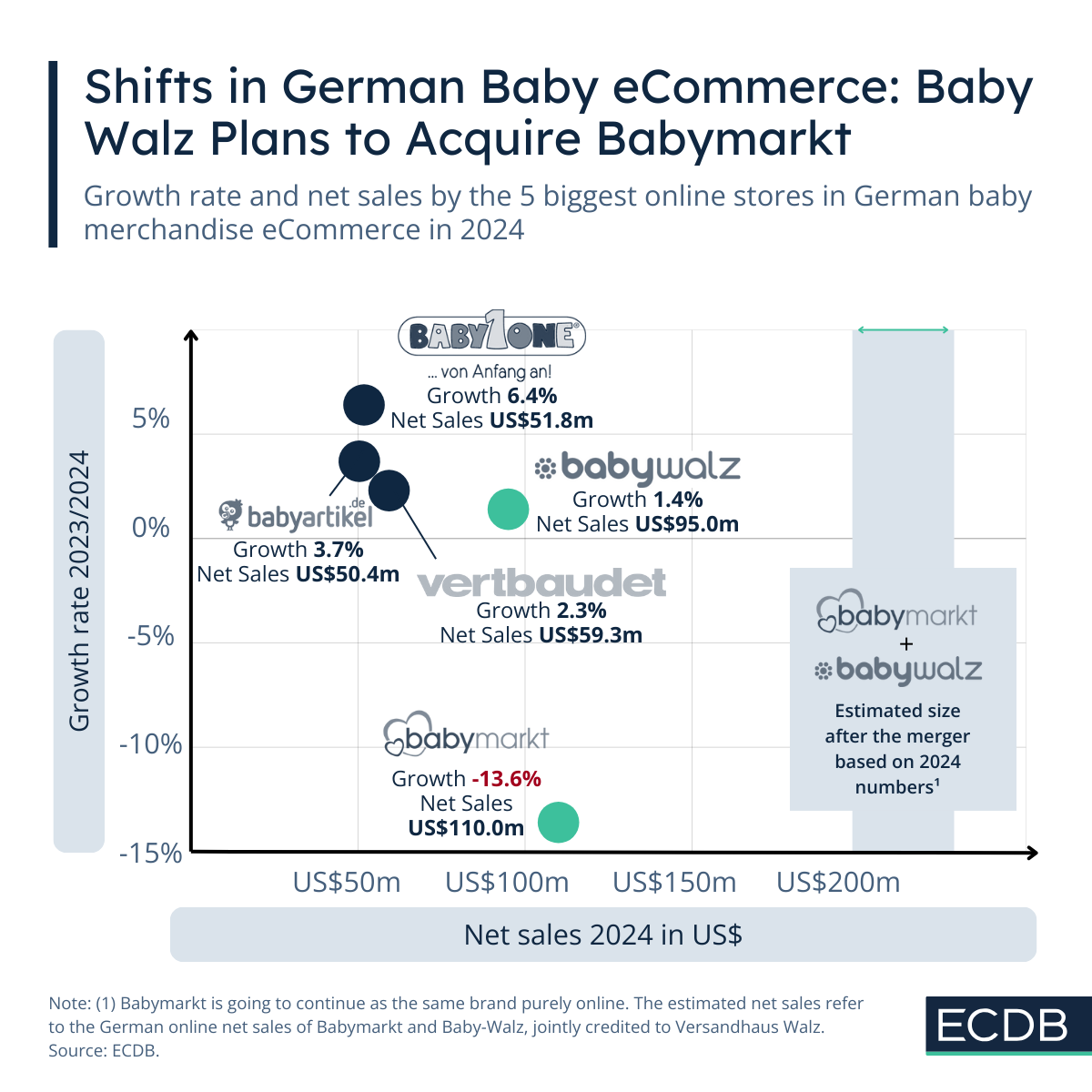
Acquisition of Babymarkt by Baby Walz: How That Changes Market Dynamics
Ready To Get Started?
Find your perfect solution and let ECDB empower your eCommerce success.