Technological innovation has created and continually shaped eCommerce over the past few decades, and as the machines we use every day become more sophisticated, so do attempts to illegally gain advantage through online fraud schemes. Phishing schemes and money laundering were well known already before the introduction of AI into the game, but recent innovations in machine learning (ML) and related systems have expanded the reach of fraudulent activity.
This article takes a closer look at machine learning to explore how AI is being used to perpetrate fraud and how merchants in turn are using it to combat attacks on their businesses.
Machine Learning Has Entered the Chat
Machine learning has gained widespread popularity in recent years due to the availability of user-friendly software. ML is a branch of artificial intelligence that enables computers to learn and improve from data, just like humans learn from experience and information. Rather than being explicitly programmed, ML algorithms are trained using structured data. These algorithms analyze the data, identify patterns, and make predictions or take actions based on what they have learned.
Neural networks, which are a more advanced subset of ML, are designed to simulate the workings of the human brain. Similar to how our brains process information through interconnected neurons, neural networks process data through layers of artificial neurons. In neural networks, an input is fed into the system and processed through multiple layers of artificial neurons, ultimately producing an output. Typically, neural networks have at least three layers, but they can be more complex and extensive.
Deep learning, a type of neural network, is characterized by its complexity. It consists of multiple layers that progressively analyze and interpret data, continuously refining their responses without requiring human intervention. Unlike traditional ML, deep learning does not rely heavily on pre-structured data or constant human supervision. This aspect makes it more accessible to individuals without extensive technical backgrounds to leverage this technology.
Machine Learning: Fraud or Fraud Prevention?
Data from Cybersource’s Global Fraud and Payments reports show that from 2022 (35%) to 2023 (43%), a higher percentage of global merchants reported experiencing Phishing attacks, which is the most common type of fraud to begin with. The 8-percentage-point year-over-year increase may be due, in part, to machine learning algorithms that make it easier to send mass messages designed to extract private user information.
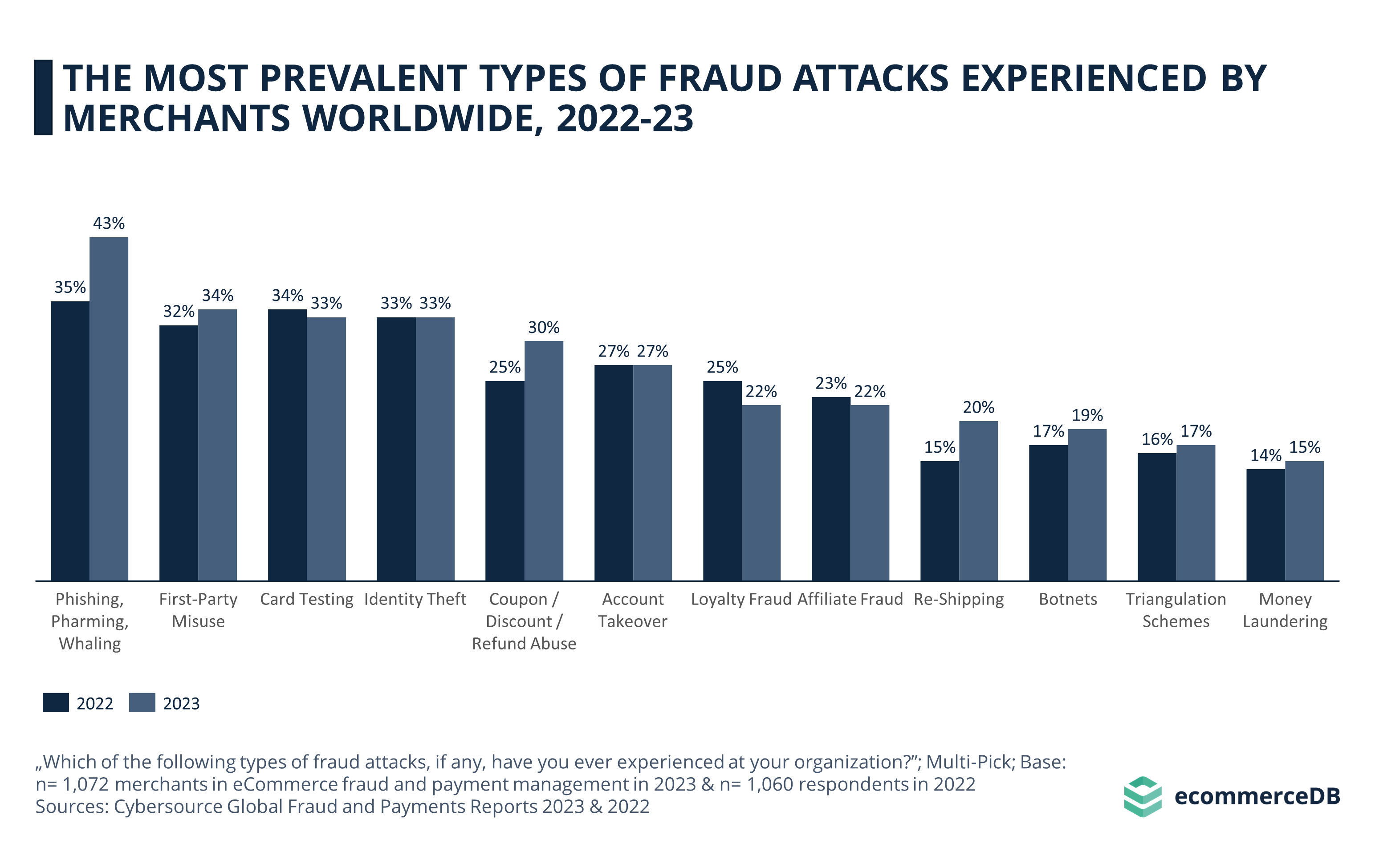
Coupon / Discount / Refund abuse also saw a large increase of 5 percentage points. Automated processes can expand the scope of refund requests, so while it is not possible to indicate based on the data at hand whether machine learning was used in some of these scams, it is not unlikely.
Re-Shipping Fraud increased by 5 percentage points, after starting from a low base of 15% in 2022. Botnets, Triangulation Schemes, and Money Laundering are the three least common types of fraud attacks, which were reported at only slightly higher rates by merchants in 2023 since 2022.
Looking at how merchants are attempting to prevent fraud through authorized payment approaches, we see that machine learning is playing a significant role in this part of the playing field as well. With an increase of 6 percentage points since 2022, machine learning tools to automatically detect suspicious transactions or accounts are reported by 41% of global merchants in 2023.
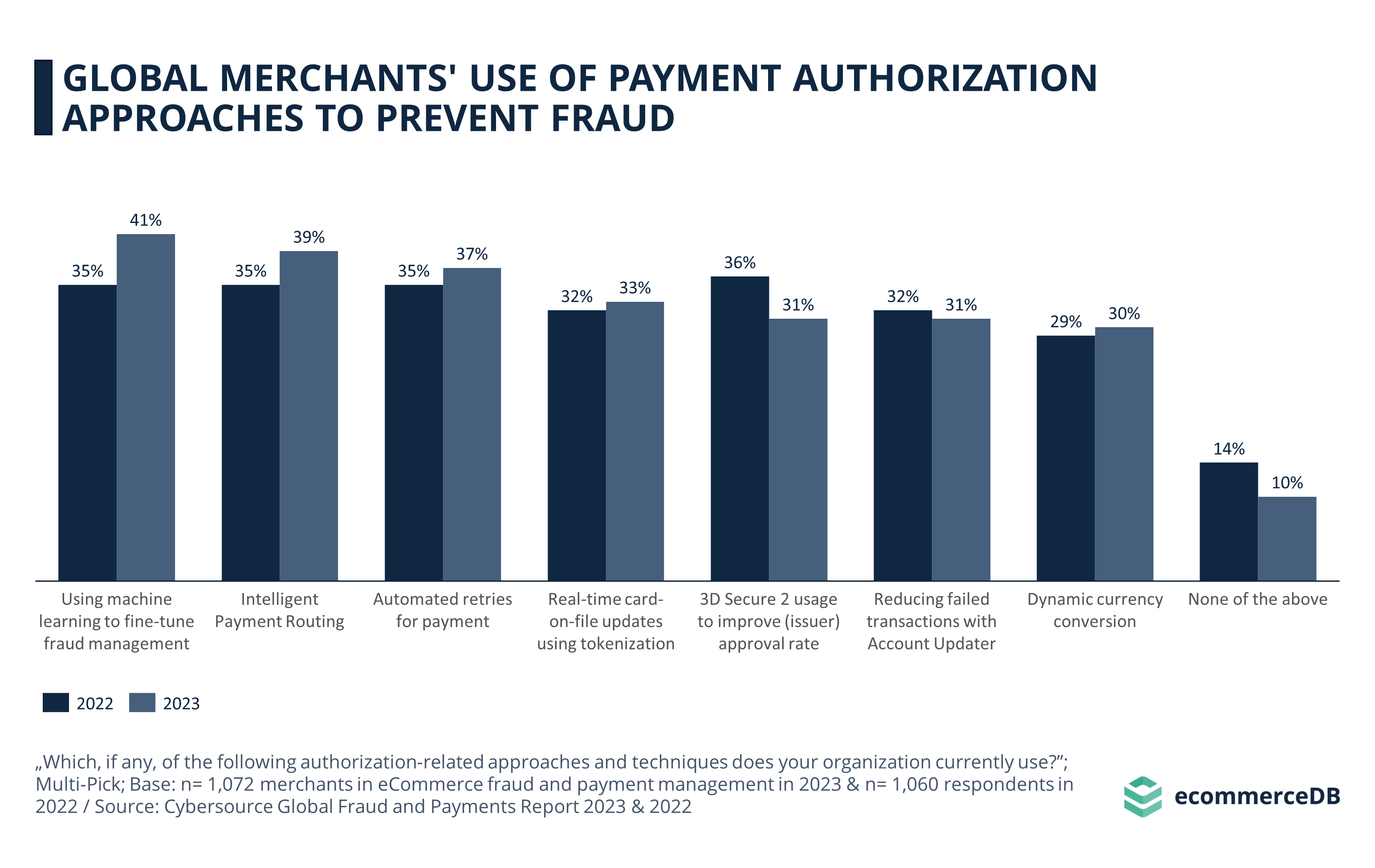
Intelligent Payment Routing is an automated process that selects the bank that is most likely to approve the payment to process a transaction, and if declined, the algorithm routes the request to another bank. 39% of global merchants use this tool in 2023, up from 34% in 2022.
The third most common approach is another AI-process that initiates an automated retry for failed payments. Note that the top three most-used tools are all automated processes, and the numbers are up from the previous year’s automated tools. At the same time, compared to 2022, fewer merchants are using none of the authorization methods listed, a trend that highlights the importance of keeping up with technological advances in eCommerce.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Using AI to Prevent Fraud
Machine learning is an advanced form of artificial intelligence that is characterized by the enhanced data processing capabilities of computers that mimic human learning processes based on information and experience, continuously improving existing capabilities through more data input. Neural networks are a subset of machine learning, which model neurons that process inputs to produce outputs, offering predictions and actions based on internal processing improvements. Deep learning consists of many internal neurons that can work on vast amounts of unstructured data, and thus can be used by people without a technical background to oversee the learning process.
Naturally, as artificial intelligence systems become more sophisticated and able to operate unattended, this facilitates their use for fraud attacks, which is simultaneously seen in the increased reporting of Phishing attacks, Coupon / Discount / Refund abuses, and Re-Shipping Fraud by global merchants. As all of these attacks allow for automated execution, their increased volume and sophistication can be exploited by fraudsters.
However, machine learning is also being used by a growing number of merchants to automatically detect suspicious transactions or accounts, as well as for Intelligent Payment Routing and automated retries of failed payments. These findings show that as technology continues to advance in the eCommerce space, it’s important to stay on top of the latest fraud prevention tools and approaches.
Sources
Related insights
Article
eCommerce Market in Europe 2024: Worth 1 Trillion Dollars Soon
eCommerce Market in Europe 2024: Worth 1 Trillion Dollars Soon
Article
In-Game Purchases Analysis: Walmart Dives Into Roblox
In-Game Purchases Analysis: Walmart Dives Into Roblox
Article
Top Online Payment Methods in the UK: Digital Wallets Challenge Cards
Top Online Payment Methods in the UK: Digital Wallets Challenge Cards
Article
Cryptocurrencies in the United States: Revenue Development, Top Currencies, Acceptance in eCommerce
Cryptocurrencies in the United States: Revenue Development, Top Currencies, Acceptance in eCommerce
Article
Global PayPal Usage: Germany Leads in Online Store Acceptance
Global PayPal Usage: Germany Leads in Online Store Acceptance
Back to main topics