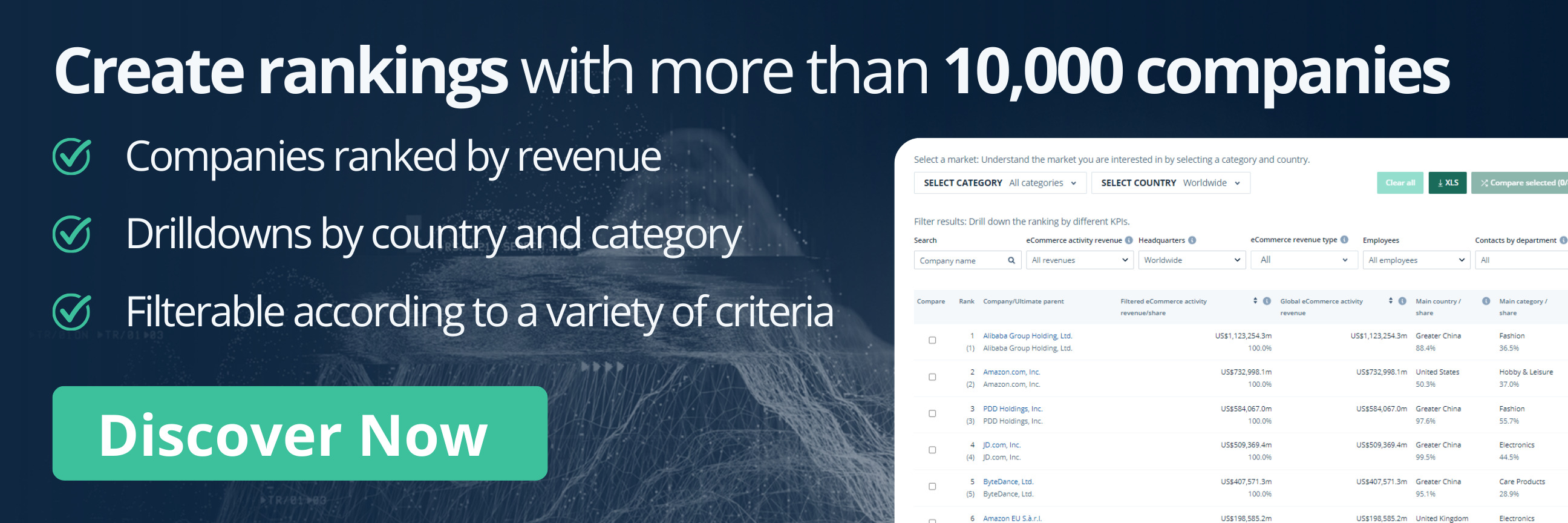
eCommerce: Revenue Analysis
Amazon Business Segments: Domain Growth, Seller Statistics & Prime
Amazon recently announced it increased revenues across its business segments in the second quarter of 2024. But what does its business consist of? Here is how Amazon makes money.
Article by Nadine Koutsou-Wehling | August 14, 2024Download
Coming soon
Share

Amazon Business Analysis: Key Insights
eCommerce Net Sales Growth: eCommerce is Amazon's revenue basis. More than 60% of revenues came from Amazon's online store domains, subsidiaries, and marketplace in 2023.
Amazon.com Performs Best: In terms of first-party net sales, where Amazon acts as the seller, and third-party net sales, where Amazon earns a per-sale commission for marketplace provision, amazon.com is the top domain. It generated the highest net sales and GMV (gross merchandise volume).
Prime Memberships: About 170 million users are Prime members in the United States. But membership is on the decline.
Amazon Seller Statistics: A majority of Amazon sellers use the platform supplement to their core business. Amazon sellers can be small and large businesses, they can sell products either directly to Amazon or to consumers via Amazon's online marketplace, and most source their products from China.
Amazon recently released its second quarter earnings results. The U.S. eCommerce leader reported that eCommerce revenues grew, with only a slight increase in operating expenses. Revenue increased in Amazon's North American segment and internationally. The company's cloud computing division saw revenue increases, as did revenues from its physical stores, marketplace, subscription, and advertising services.
With all these variables, one might wonder what business segments Amazon is managing. Here is how the eCommerce giant makes money.
Amazon’s Business Segments: A Revenue Breakdown
Amazon was one of the winners of the 2020 pandemic, as it was able to increase its revenues across all of its business segments. With earnings already substantial at US$267 billion in 2019, this figure reached US$523 billion by 2023, growing by an average of US$64 billion each year up to 2023.
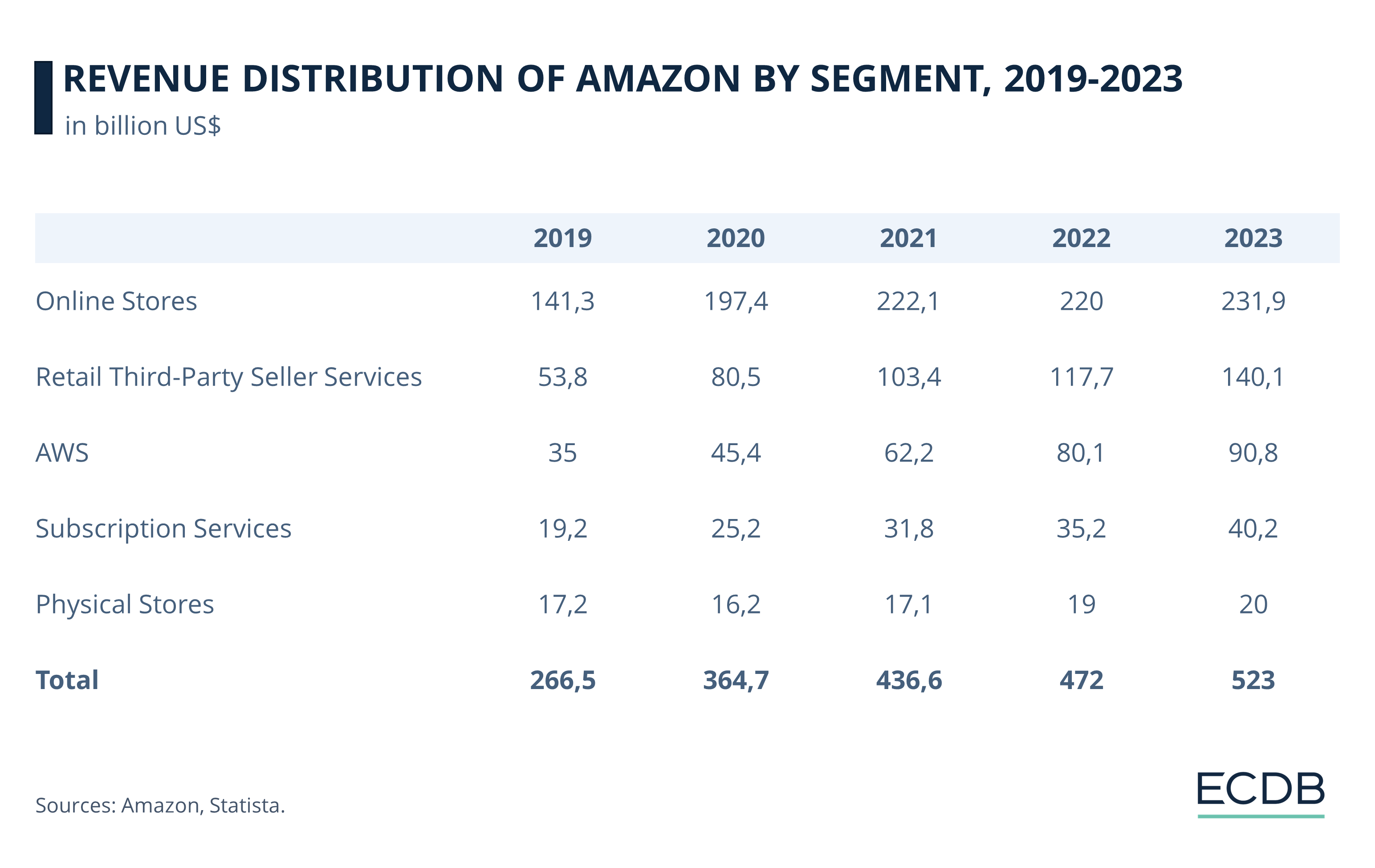
The company has a diverse portfolio of businesses, ensuring steady revenue streams and leveraging economies of scale to compete with other players in each area. Amazon’s competitiveness stems from the fact that it is known for offering the latest innovations at affordable prices.
Amazon’s online stores include its various international domains on the one hand, as well as numerous acquisitions the company has made over the years. In this way, Amazon is involved in most relevant sectors of the economy, including fashion, technology, and groceries. Amazon’s eCommerce net sales subsequently account for the largest share of its revenue, reaching 44% by 2023.
While Amazon has also ventured into physical store sales, such as its Amazon Go and Go Grocery stores, Amazon Fresh, and its subsidiary Whole Foods Market, it is clear that the conglomerate’s primary business is online. In particular, Amazon’s online marketplace stands out, where third-party retailers sell their products and Amazon earns a commission for providing technology and related services. In 2023, Amazon generated US$140 billion from these commissions, and the marketplace’s gross merchandise volume (GMV) points to continued growth, but more on that later.
Subscription services and AWS (Amazon Web Services), its cloud computing arm, make up the remaining quarter of revenues.
Amazon.com Is the Best-Selling Domain
Amazon’s online net sales across all of its domains account for the largest share of revenue, so they are worth breaking down. The top 10 Amazon domains by eCommerce net sales are as follows:
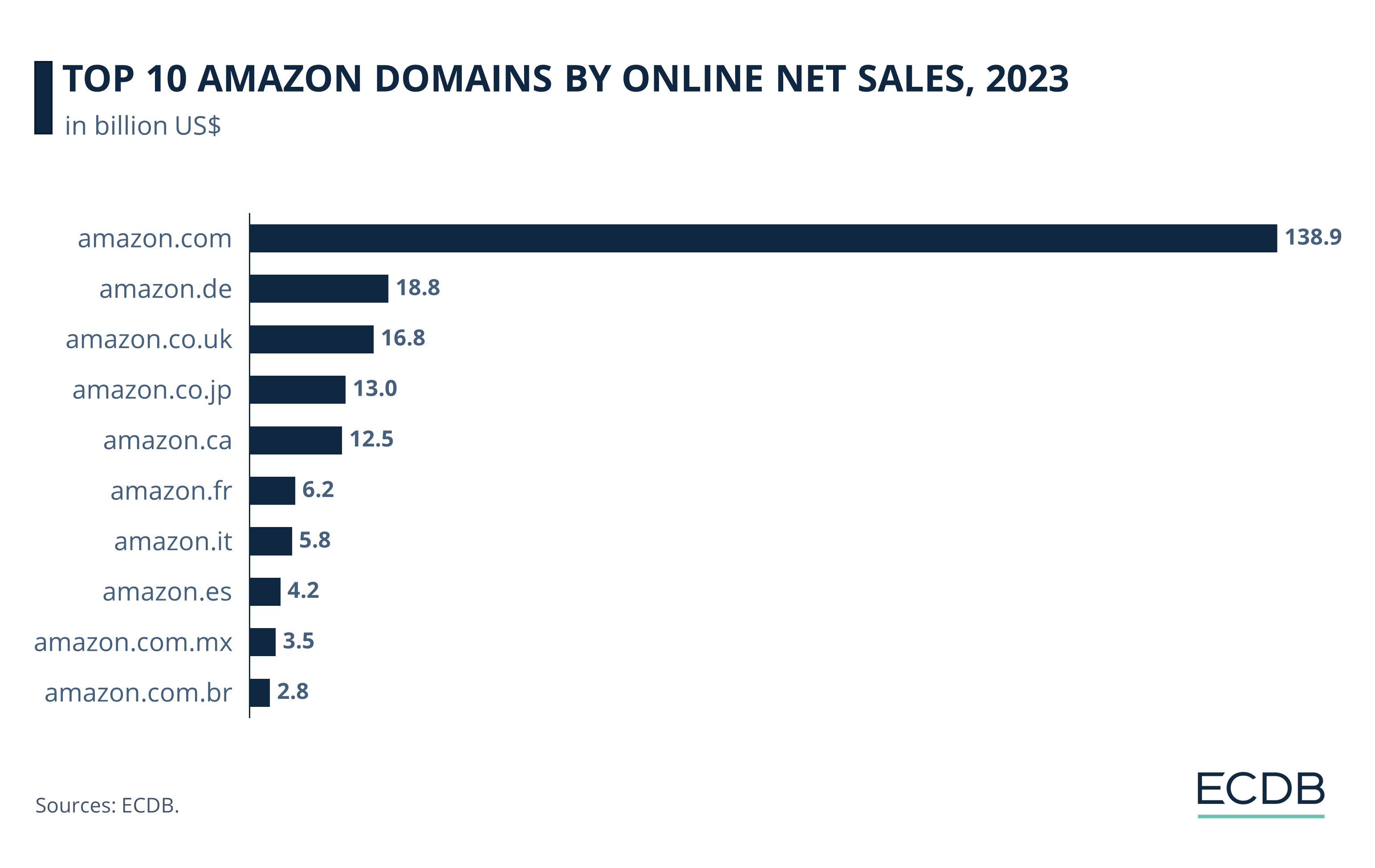
Amazon.com is the domain with the highest net sales, dwarfing the others with 2023 revenues of US$138.9 billion. The other markets generate only a fraction of this figure, with amazon.de in second place, approaching US$19 billion in online net sales.
The UK domain comes in third (US$16.8 billion), followed by amazon.co.jp (US$13 billion) and amazon.ca (US$12.5), rounding out the top 5 Amazon domains by revenue.
The other half of Amazon’s top 10 domains consists of amazon.fr (US$6.2 billion), amazon.it (US$5.8 billion), amazon.es (US$4.2 billion), amazon.com.mx (US$3.5 billion), and amazon.com.br (US$2.8 billion).
Amazon.com Is Also Top Marketplace by GMV
Amazon also functions as a marketplace provider, whose performance is measured by GMV. It is a metric to gauge marketplace activity.
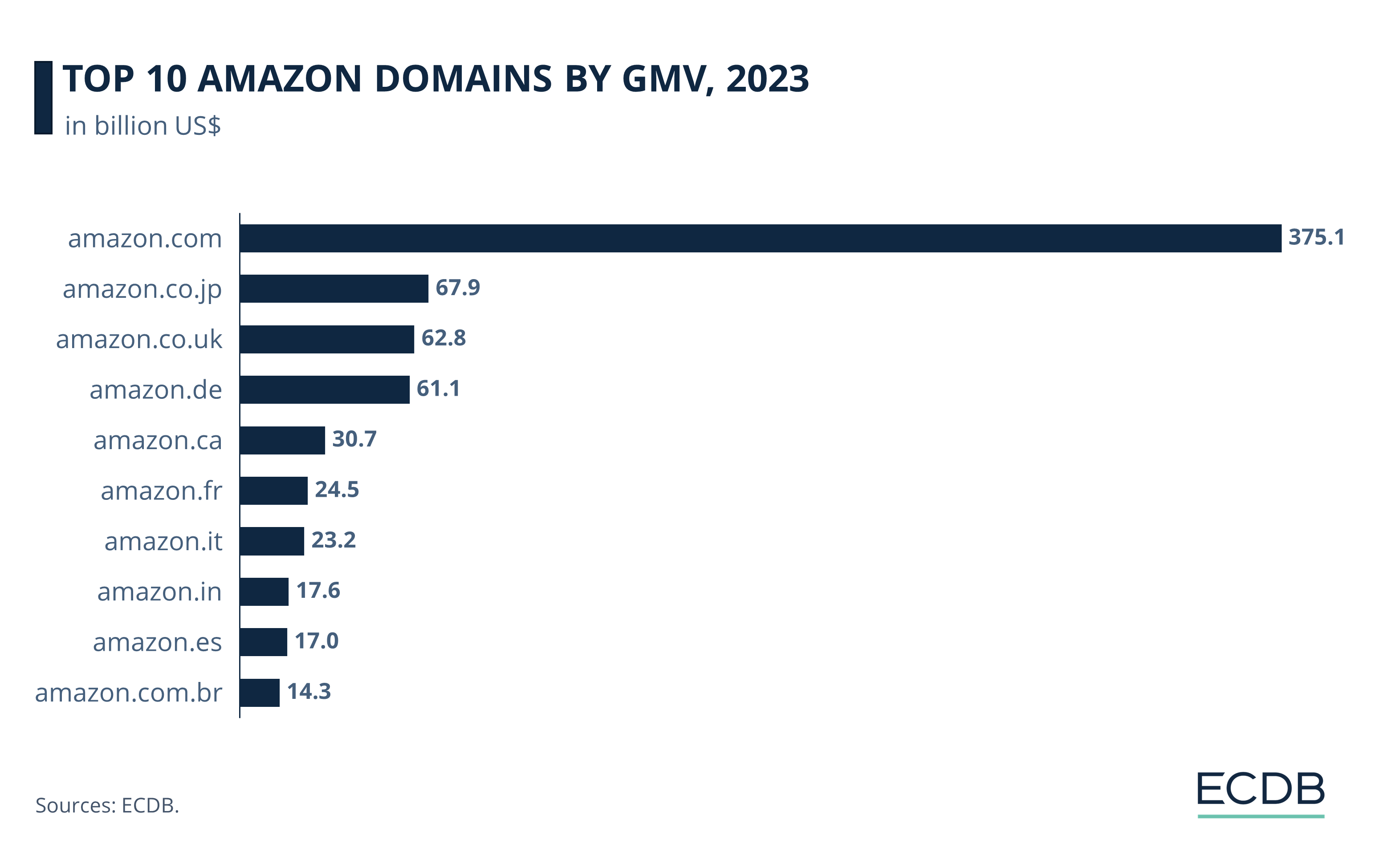
As with first-party net sales, amazon.com takes the lead as marketplace, with US$375.1 billion worth of products sold in 2023. This figure corresponds to the annual value of import and export revenues for countries like Vietnam.
Amazon.co.jp is the second largest Amazon marketplace by GMV, with US$67.9 billion in third-party sales in 2023, followed by amazon.co.uk in third place (US$62.8 billion). Amazon.de, which ranks second in first-party sales, is Amazon’s fourth largest marketplace with a GMV of US$61.1 billion. Fifth is amazon.ca, with a GMV of US$30.7 billion in 2023.
The remaining marketplaces in the top 10 by GMV are amazon.fr (US$24.5 billion), amazon.it (US$23.2 billion), amazon.in (US$17.6 billion), amazon.es (US$17 billion), and amazon.com.br (US$14.3 billion).
Amazon takes a per-sale commission as well as vendor services such as shipping, warehousing, and sales analytics. Therefore, although the GMV is higher than the online net sales in the previous section, Amazon earns a fraction of it for its function as a marketplace provider.
Shoppers receive extra benefits when they shop on Amazon with a Prime membership. What are the usage numbers for this service?
Nearly 170 Million Prime Members in the United States
A Prime membership offers delivery benefits, ad-free access to Prime Video, Prime Reading and Amazon Music, as well as Amazon Photos and Prime Gaming. The annual Prime Day discount event is a major driver of new memberships.
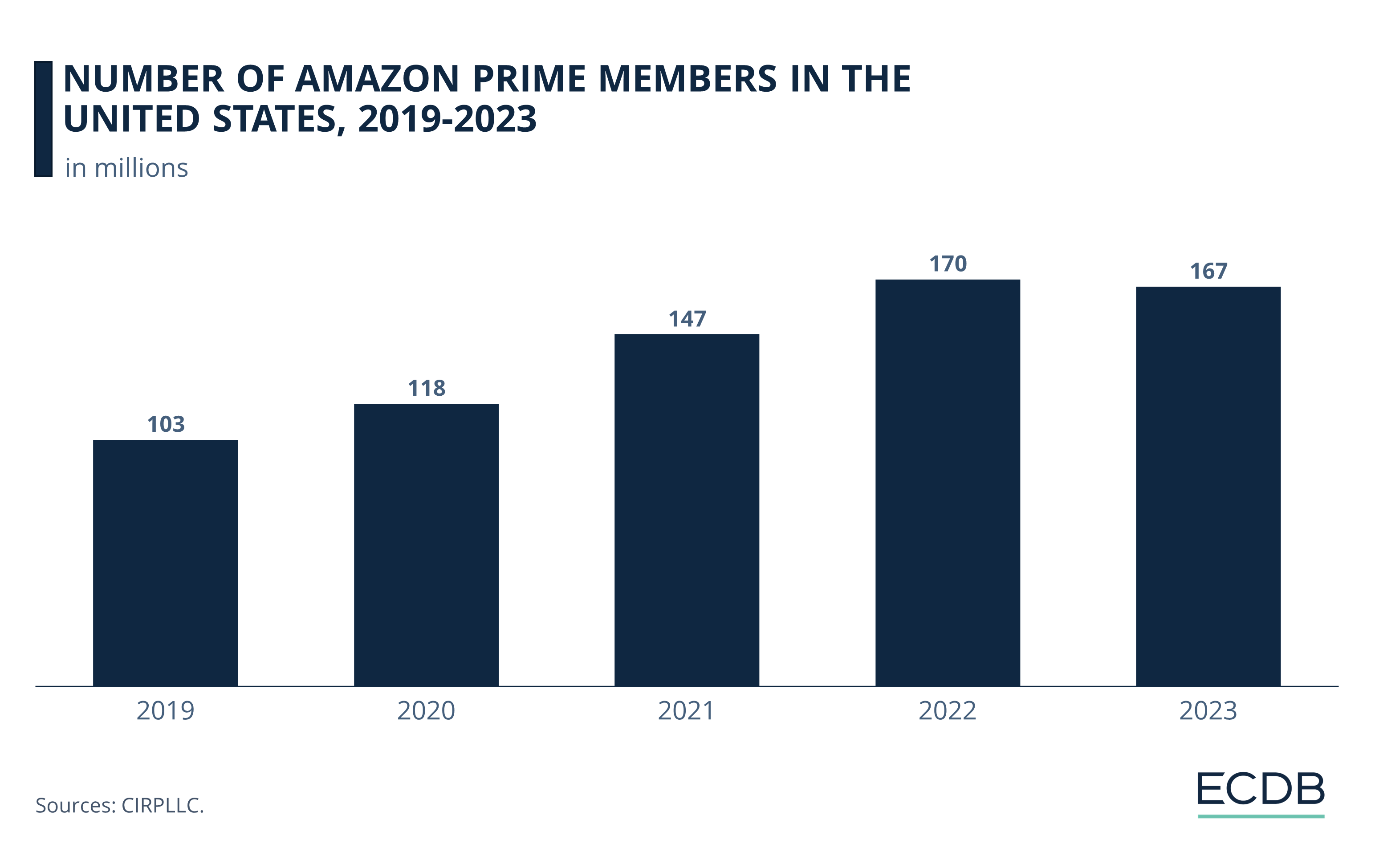
The number of Amazon Prime members in the United States saw a temporary spike in 2022, when 170 million subscribers used the service. This was a 61% increase from 2019, when 103 million Prime members were recorded.
However, there was a slight drop in user numbers in 2023. While Prime memberships only declined by a small margin, and Amazon disputed the downward trend noted by CIRP, the retail giant was unable to provide evidence to the contrary. Analysts have suggested that recent increases in Prime membership fees may have contributed to the decline in membership.
Because of the wide range of services included in its Prime membership program, Amazon has many competitors where consumers may feel they are getting a better deal. One of the key features of a Prime subscription is exclusive access to its own video and music streaming platforms.
Growing Budget for Prime Streaming Content
Competing with the likes of Netflix, Disney+, HBO, Hulu and others, Amazon Prime is not only a streaming platform, but also produces its own content based on audience feedback. In 2021, Amazon acquired film studio MGM, expanding its exclusive rights to a larger pool of titles.
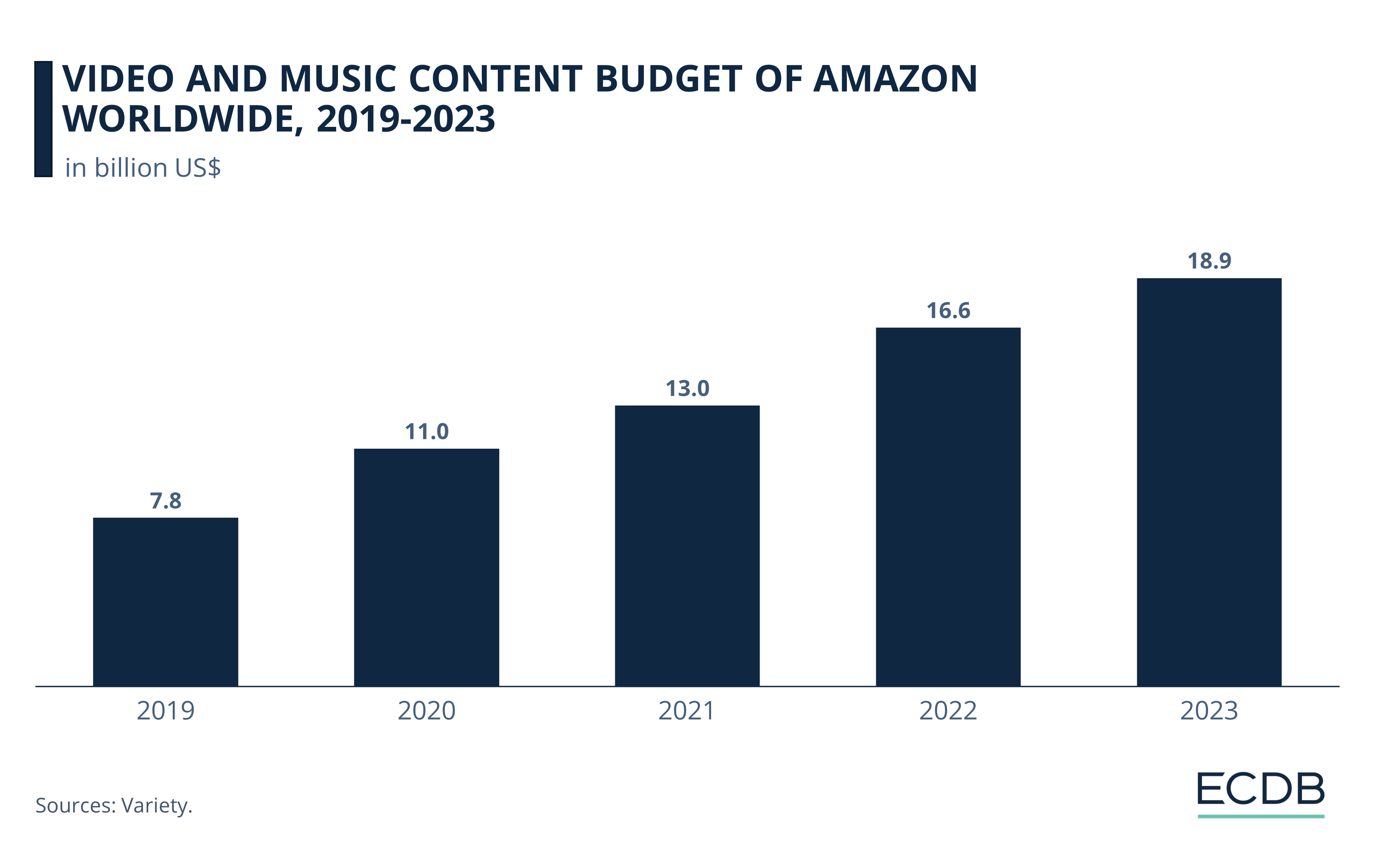
Together with Amazon Music, a growing budget is available for the streaming content accessible to Prime users, reaching US$18.9 billion in 2023. This is made possible in part by the massive acquisitions Amazon has made over the years.
Amazon Subsidiaries Ring and Zappos Exceeded US$1 Billion in 2023
The various subsidiaries and associated external domains should not be underestimated in their contribution to Amazon’s online store revenues.
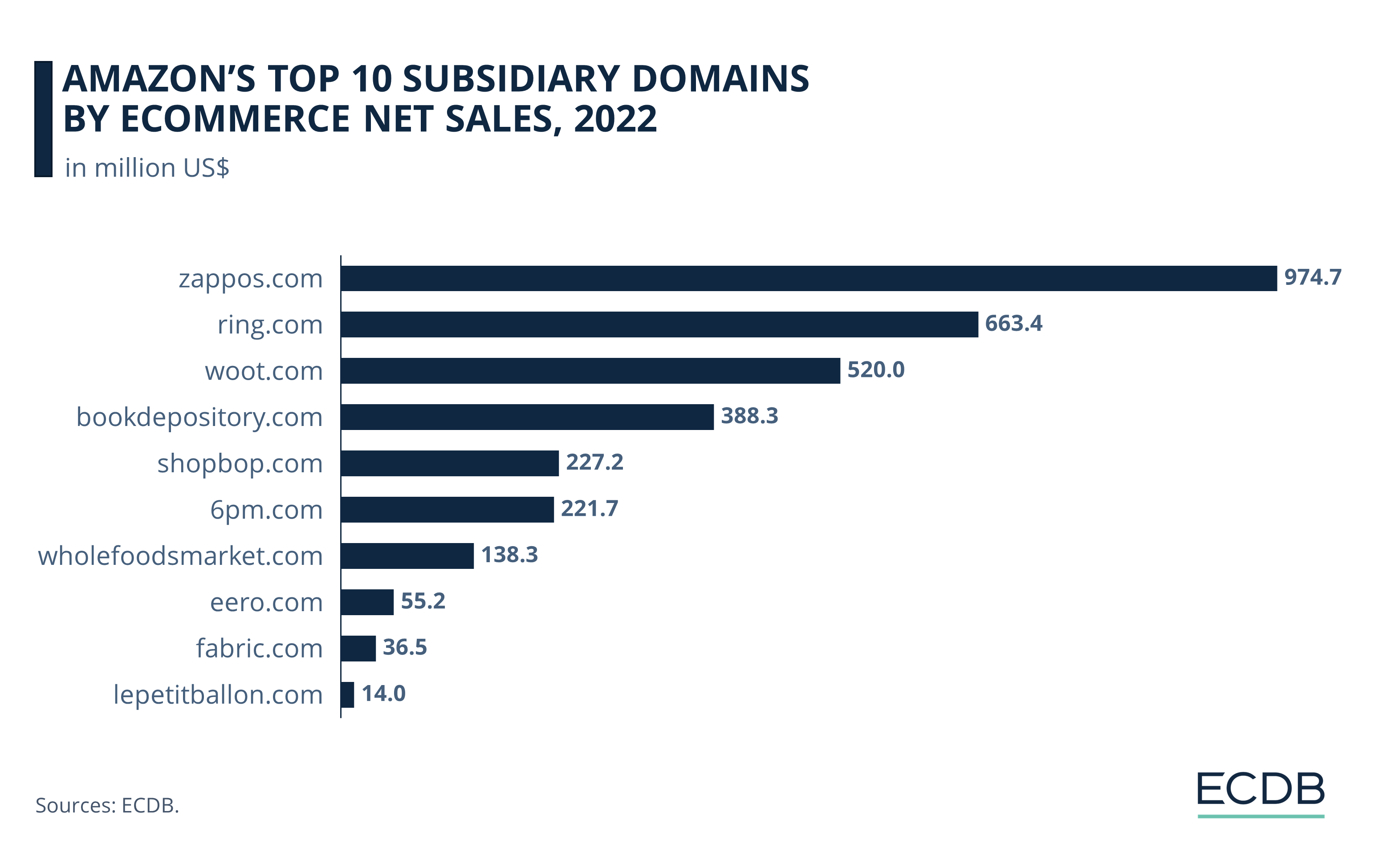
Note that these top domains are among over 100 subsidiaries that Amazon has acquired over the years. Many are second-tier subsidiaries, meaning that a daughter company of Amazon acquired them, making Amazon the ”grandparent company”. There are also third-tier subsidiaries that were acquired by second-tier subsidiaries.
Amazon: Top External Domains by Online Net Sales in 2023
Note that this refers to online sales of physical products only, and therefore excludes Amazon subsidiaries such as Audible, Twitch or Goodreads, which fall out of the scope of ECDB's definition of eCommerce.
1. Ring.com
Two external domains stand out in terms of eCommerce net sales: The first is ring.com, a smart home technology retailer. Ring saw a significant year-over-year increase in revenue in 2023, when it generated eCommerce revenues of US$1.1 billion. The 65.4% rise in net sales can be attributed to the high relevance of Ring's innovative technology offerings, which include mobile-controlled security cameras, alarm systems, and intercoms.
2. Zappos.com
Following in second place is zappos.com, an online shoe store that Amazon bought in 2009. The shoe store approached the billion-dollar mark with online net sales of US$974.7 million in 2022 and surpassed it in 2023, reaching US$1.06 billion eCommerce net sales.
3. Woot.com
Third rank is woot.com, a retailer with a diverse product assortment consisting of electronics, home goods, and apparel, with US$584.5 million in 2023.
4. Shopbop.com
In fourth place is shopbop.com, a high-end clothing and beauty products brand, which generated US$236.8 million in 2023.
5. 6pm.com
Close behind in fifth place is 6pm.com, a second-tier subsidiary acquired by Zappos.com, LLC that operates as an online marketplace for discount retailers. 6pm.com made US$188.5 million in online net sales in 2023.
6. Wholefoodsmarket.com
Further down the list is organic foods retailer Whole Foods Market, an established grocer with an extensive brick-and-mortar presence that was acquired by Amazon in 2017. In 2023, wholefoodsmarket.com generated US$157.4 million.
7. Bookdepository.com and Other Closures
Bookdepository.com ranked fourth in 2022 with online net sales of US$388.3 million, but the store was closed in 2023 amid a wave of closures involving Amazon’s devices and books segments. This results in a last eCommerce net sales value of US$92.2 million in 2023. Closures also affected some of Amazon’s physical stores, including its Amazon Style locations, and fabric.com, which sold apparel fabrics but was discontinued in 2022.
Remaining Placements: Eero and Lepetitballon
The remaining placements on the 2023 list include eero.com (US$76.4 million) and lepetitballon.com (US$12.9 million). Eero sells easy-to-use WiFi routers and Le Petit Ballon is a French wine store that connects customers with wine sellers over the internet.
For your information: We regularly update our rankings with the latest data from our models, providing valuable insights to help improve your company. Which stores and companies are leading eCommerce? Which categories are driving bestsellers and high sales? Find out for yourself on our rankings for companies, stores, and marketplaces. Stay a step ahead of the market with ECDB.
Most Products on Amazon Come From China
Jungle Scout conducted a survey of Amazon sellers and brands to examine their relationship with Amazon. One of the areas of inquiry was the origin of the products that sellers offer on Amazon.
Brands can source their products from multiple countries, which is why the values in the chart exceed 100%.
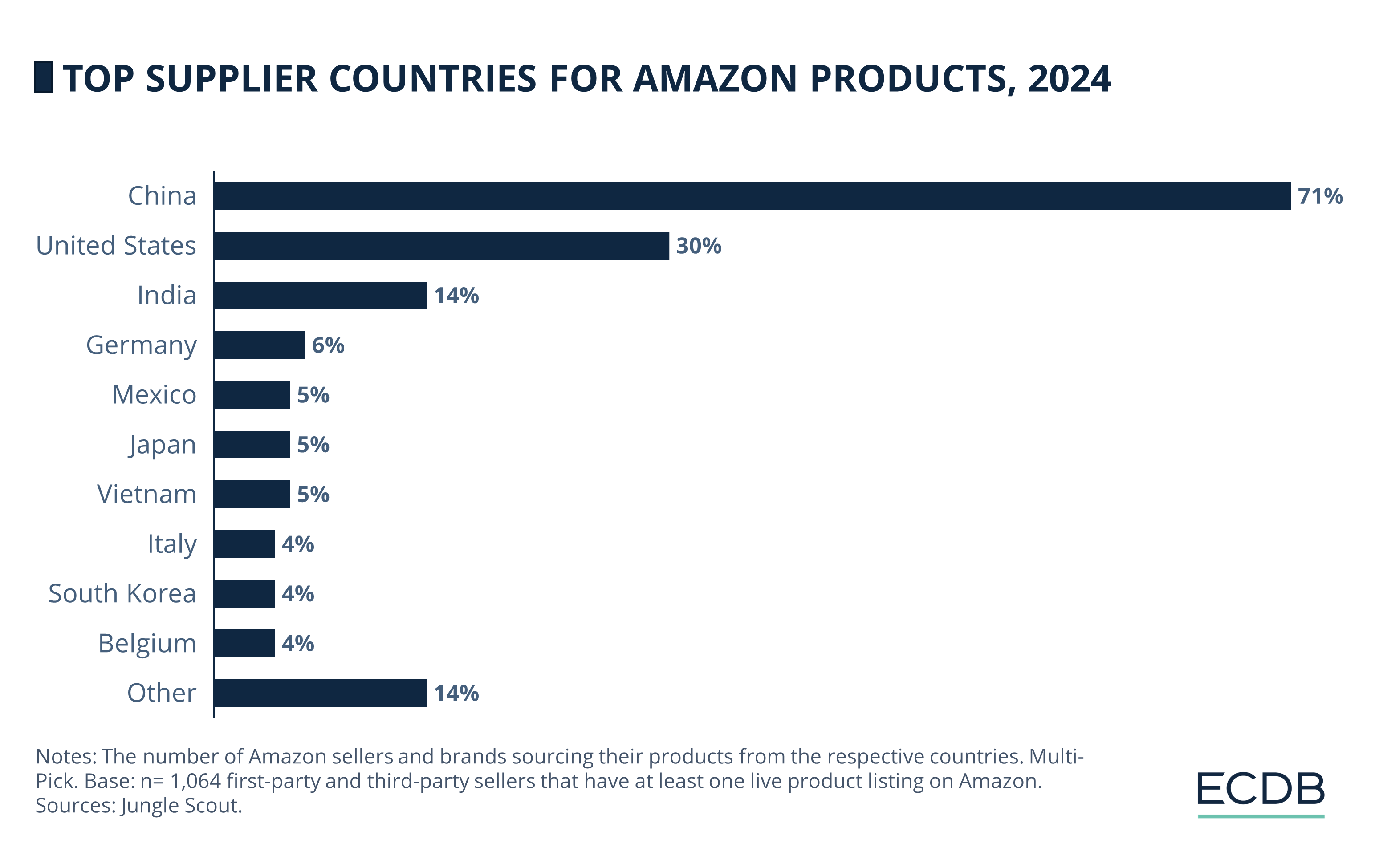
China is by far the most common country of origin for products sold on Amazon, cited by 71% of sellers and brands. Further behind is the United States, mentioned by 30% of Amazon sellers and brands. India is the next country that stands out, with a 14% share.
Rankings 4-10 indicate mostly similar shares, starting with Germany at 6%, through Mexico, Japan, and Vietnam at 5%, and ending with Italy, South Korea, and Belgium at 4%. Other countries account for 14% of sellers and brands selling on Amazon.
Amazon’s broad reach and established position as a retailer and shipping provider are persuading brands of all kinds to sell their products on the platform. But how much significance does Amazon have for its affiliate sellers?
Amazon Is Mostly Used by Sellers as an Additional Retail Channel
The reasons for selling products on Amazon as a third-party or first-party retailer are varied, ranging from using Amazon as an additional channel to selling products on Amazon as a main business.

Responses regarding the importance of Amazon product listings to sellers' overall business are evenly distributed in terms of frequency. At the top of the list, with 34% of sellers and brands agreeing, is selling on Amazon as an adjunct to an established D2C site.
Almost as many respondents, 33%, say their Amazon sales are used for seasonal or promotional distribution of their products, while another 33% say Amazon is a strong channel used in conjunction with other online or offline ventures.
In third place are 32% of brands and sellers who consider Amazon their primary sales channel. This is followed by 31% who use Amazon as a tool for international expansion and new markets, while 30% test sell products on the platform to gauge product popularity before a wider release.
Business Size: Large Sellers Use More Diverse Advertising Methods
Amazon distinguishes between two types of sellers based on company size: Amazon Sellers & SMB (Small to Medium-Sized Businesses), which are either individual entrepreneurs or small businesses, and Enterprise Brands & Retailers, which are larger corporations or conglomerates.
Both these types of sellers can sell their products to Amazon as first-party sellers or third-party sellers. The first-party type sells merchandise directly to Amazon, which Amazon offers to customers as its own brand and earns revenue as a retailer. The third-party type sells products to customers through Amazon’s online marketplace, from which Amazon earns a commission as a marketplace provider.
The top channels through which Amazon businesses advertise their products are broken down by company size:
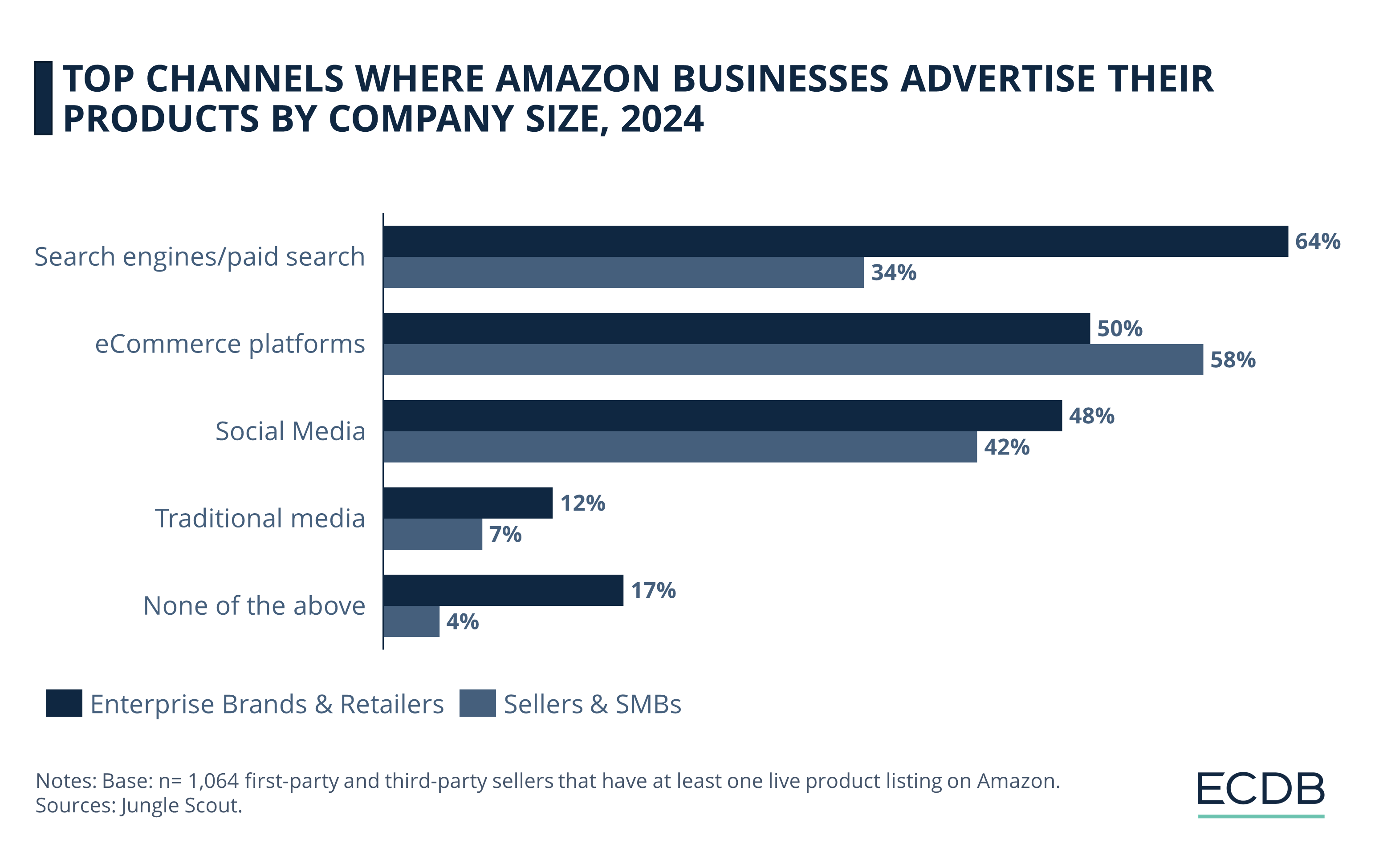
For larger businesses, i.e. Enterprise Brands & Retailers, the most common advertising channel is search engines or sponsored search results (64%), while this channel is about half as popular for smaller businesses (34%).
Small companies tend to promote their products on eCommerce sites (50%), similar to 58% of large companies. Retail media advertising is also a field in which Amazon has major stakes, contributing a portion of total revenues.
Advertising on social media is similarly used by both small and large businesses, with 48% of large businesses and 42% of small businesses agreeing.
While it is also more common for large companies to advertise in traditional media (12%), small businesses are less likely to do so (7%). However, larger companies are also the ones saying they do not use any of the above advertising methods, at 17%, compared to only 4% of small businesses.

Amazon Business Analysis:
Closing Remarks
Amazon stays ahead of competitors due to its economies of scale, and many established businesses seek its reach and visibility. The associated domains, businesses, and external sellers emphasize the sheer magnitude of Amazon’s influence. These are similar to Alibaba’s diverse income sources, which help mitigate financial risks. While newer players try to replicate Amazon’s product diversity and low pricing approach, Amazon’s dominance remains unmatched due to its far-reaching network and industry recognition.
Sources: Craft Industry Alliance – Forbes – Jungle Scout – NIF – Tech Crunch – The Robin Report – Wired – 6pm
Amazon Business Model: FAQs
What is Amazon's main business strategy?
Amazon's main business strategy focuses on customer centricity, innovation in services and technology, diversified business segments to generate revenues, economies of scale, subscription services, and a global expansion of its marketplace model.
What is Amazon's business model?
The business model that Amazon operates in is highly diversified, called a multi-pronged business approach. It includes online retail, where Amazon acts as a seller, and the online marketplace, where Amazon is the intermediary providing the platform for third-party sellers to offer their products to online shoppers. Amazon Prime is another major income generator for Amazon, offering membership perks like faster delivery and access to its streaming services. AWS (Amazon Web Services) is a cloud computing service for businesses and governments. Amazon also generates revenue through advertising services and offers logistics and delivery services to sellers on its marketplace, for which Amazon takes a commission. But Amazon does not exclusively operate in eCommerce. It also operates physical stores that are own-branded, as well as subsidiary stores.
What makes Amazon's strategy today so successful?
Amazon has coined the phrase "Amazonization", which means taking a customer-centric approach that values convenience, abundance of choice and immediacy. The U.S. conglomerate is known for its high efficiency and scale, which makes the services it offers profitable, attracting other businesses to participate in the expansive network. Amazon uses data analytics to better understand consumer beahvior, optimize its operations, and personalize the shopping experience. Consumers know and trust Amazon, which in turn makes it hard for smaller, lesser known companies to measure up. This further contributes to Amazon's leadership and global growth.
What is Amazon's unique selling point?
Amazon's unique selling point (USP) is its comprehensive, customer-centric ecosystem that offers convenience, selection, and value. This USP is characterized by its vast product selection, customer-centric approach, innovation and technology, Amazon Prime, Amazon marketplace, a high degree of personalization, and convenience.

Click here for
more relevant insights from
our partner Mastercard.
Related insights
Deep Dive
eCommerce in Canada: Top Stores, Market Development & Trends
eCommerce in Canada: Top Stores, Market Development & Trends
Deep Dive
Top eCommerce Companies by Market Cap 2024
Top eCommerce Companies by Market Cap 2024
Deep Dive
Online Shopping in the United States: Where Consumers Prefer to Shop Online
Online Shopping in the United States: Where Consumers Prefer to Shop Online
Deep Dive
Alibaba Competitors: Which Companies Are Alibaba’s Biggest eCommerce Rivals?
Alibaba Competitors: Which Companies Are Alibaba’s Biggest eCommerce Rivals?
Deep Dive
The Global B2B eCommerce Market: Why It Is Beneficial to Sell to Other Businesses
The Global B2B eCommerce Market: Why It Is Beneficial to Sell to Other Businesses
Back to main topics